

Special characters perform some particular tasks according to their behavior and the position where they are used. It returns logical 1 (true) if either input, or both, calculate to true, and logical 0 (false) if they do not. It returns logical 1 (true) if both inputs calculate to true, and logical 0 (false) if they do not. They are short-circuiting operators in that they calculate their second operand only when the first operand does not fully determine the output. The following operators execute AND and OR operations on logical expressions, including scalar values.

It returns the bit-wise exclusive OR of two nonnegative integer arguments. It returns the bit-wise complement as an n-bit number, where n is the second input argument to bitcmp. It returns the bit-wise OR of two nonnegative integer arguments. It returns the bit-wise AND of two nonnegative integer arguments. The examples are present in the following table use scalar inputs A and B, where If in arrays, these operations produce a like-sized output array. The following functions execute bit-wise logical operations on nonnegative integer inputs. Note: MATLAB converts any finite nonzero, mathematic values used as inputs to logical expressions to logical 1, or true. The one exception to this is where one operand is a scalar, and the other is not. It returns 1 for every element location that is true (nonzero) in only one array, and 0 for all other elements.įor operators and functions that take two array operands (&, |, and xor), both arrays must have the same dimensions, with each dimension being the same size. Logical NOT It complements each element of the input array, A. Logical OR It returns 1 for every element location that is true (nonzero) in either one or the other, or both arrays, and 0 for all other elements. Logical AND It returns 1 for every element location that is true (nonzero) in both arrays and 0 for all other elements. The examples are shown in the following table use vector inputs A and B, where The following logical operators and functions execute element-wise logical operations on their inputs to produce a like-sized output array. The values returned by MATLAB logical operators and functions, with the exception of bit-wise functions, are of type logical and are suitable for use with logical indexing.
For vectors and rectangular array, both operands must be the equivalent size unless one is a scalar. SymbolĮxcept for some matrix operators, MATLAB arithmetic operators work on corresponding functions of arrays with equal dimensions.
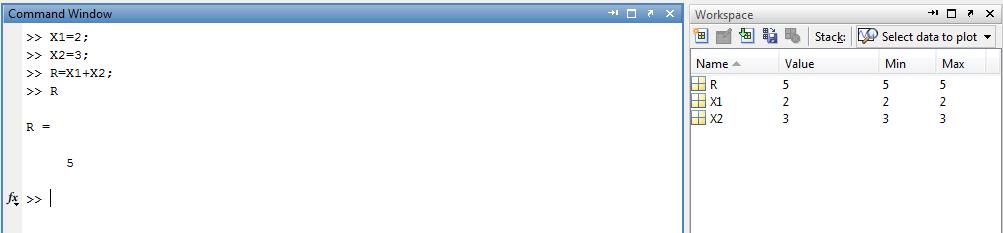
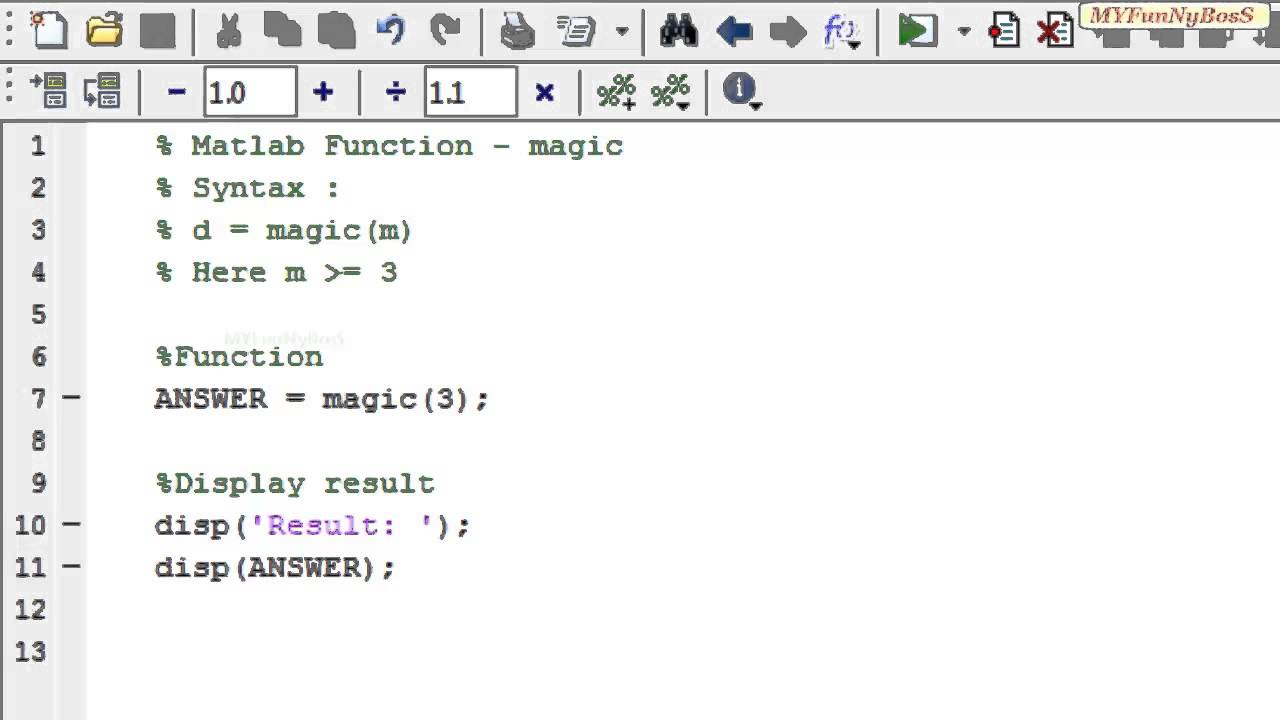
MATLAB Arithmetic OperatorsĪrithmetic operators help in performing simple arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and power. MATLAB has several types of operators, symbols, and special characters to deal with variables, functions, and arithmetic operations. Therefore, functions in MATLAB work both on scalar and non-scalar data. MATLAB is designed to operate mainly on whole matrices and arrays. An operator is a symbol that tells the compiler to perform various numerical or logical manipulations.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
